Southern Jutland's geographic advantages
at the heart of Scandinavia
Introduction
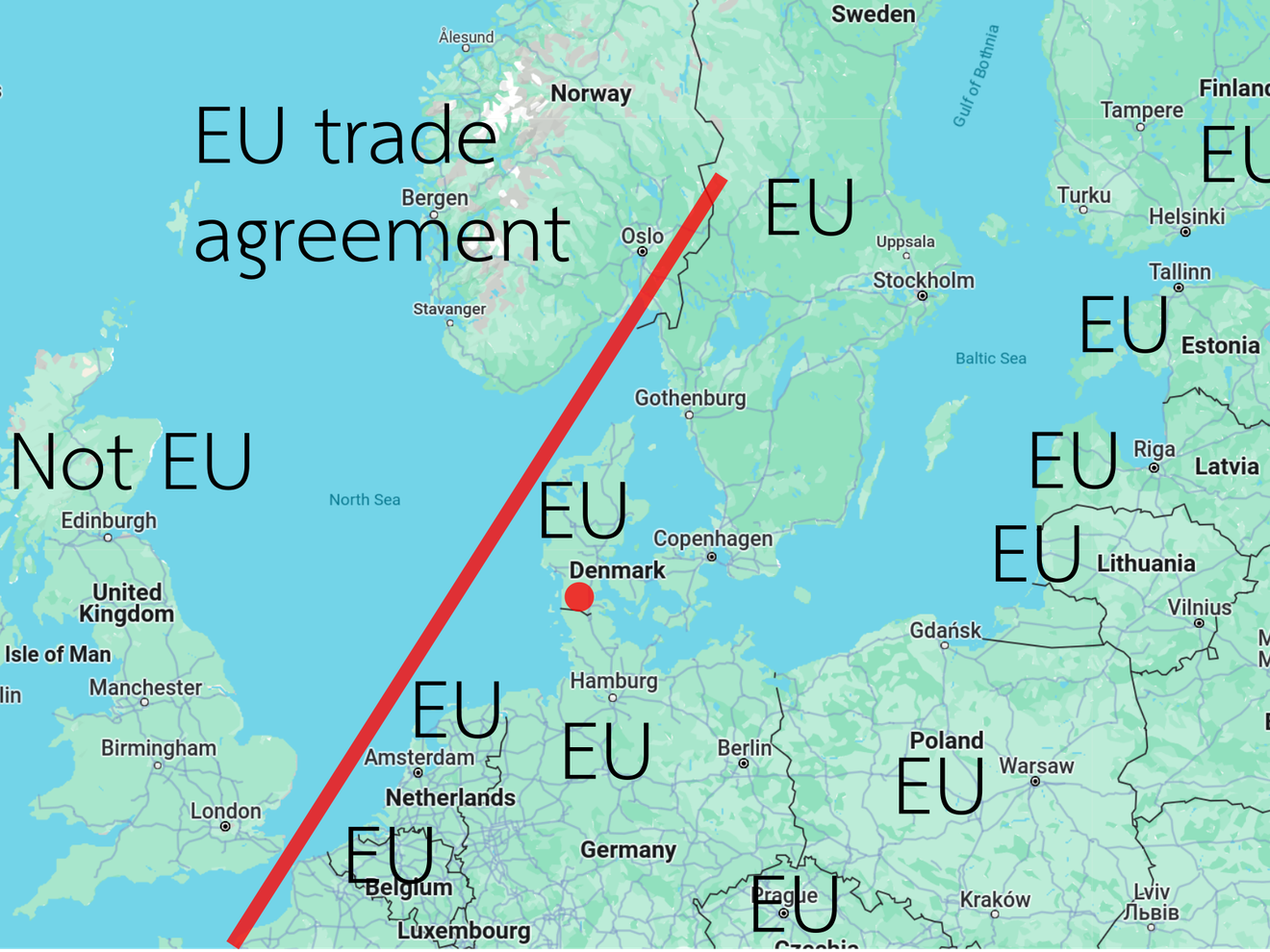
Southern Jutland, a region that uniquely straddles the border between Denmark and Germany, serves as a significant geographic and economic corridor within Scandinavia. This strategic location offers unparalleled proximity to major European markets, ease of access to robust infrastructure in both Denmark and Germany, and a well-integrated network of transport routes facilitating efficient movement of goods. This article delves into the geographic, economic, and infrastructural advantages of Southern Jutland, highlighting how its position contributes to its status as a dynamic hub in Northern Europe.
Geographic location and economic significance
Strategic position
Southern Jutland is positioned at the nexus of Scandinavian and European commerce. This region not only acts as a gateway between Denmark and Germany but also serves as a critical juncture for trade flows across Europe. Its location enables businesses to access and penetrate diverse markets efficiently, from the Nordic countries to Central Europe and beyond.
Economic integration
The economic landscape of Southern Jutland is heavily influenced by its geographic location. The region benefits from cross-border trade and economic policies that encourage cooperation between Denmark and Germany. Such integration has fostered a unique economic environment that supports a wide range of industries, from manufacturing and logistics to technology and services.
Access to major european markets
Proximity advantages
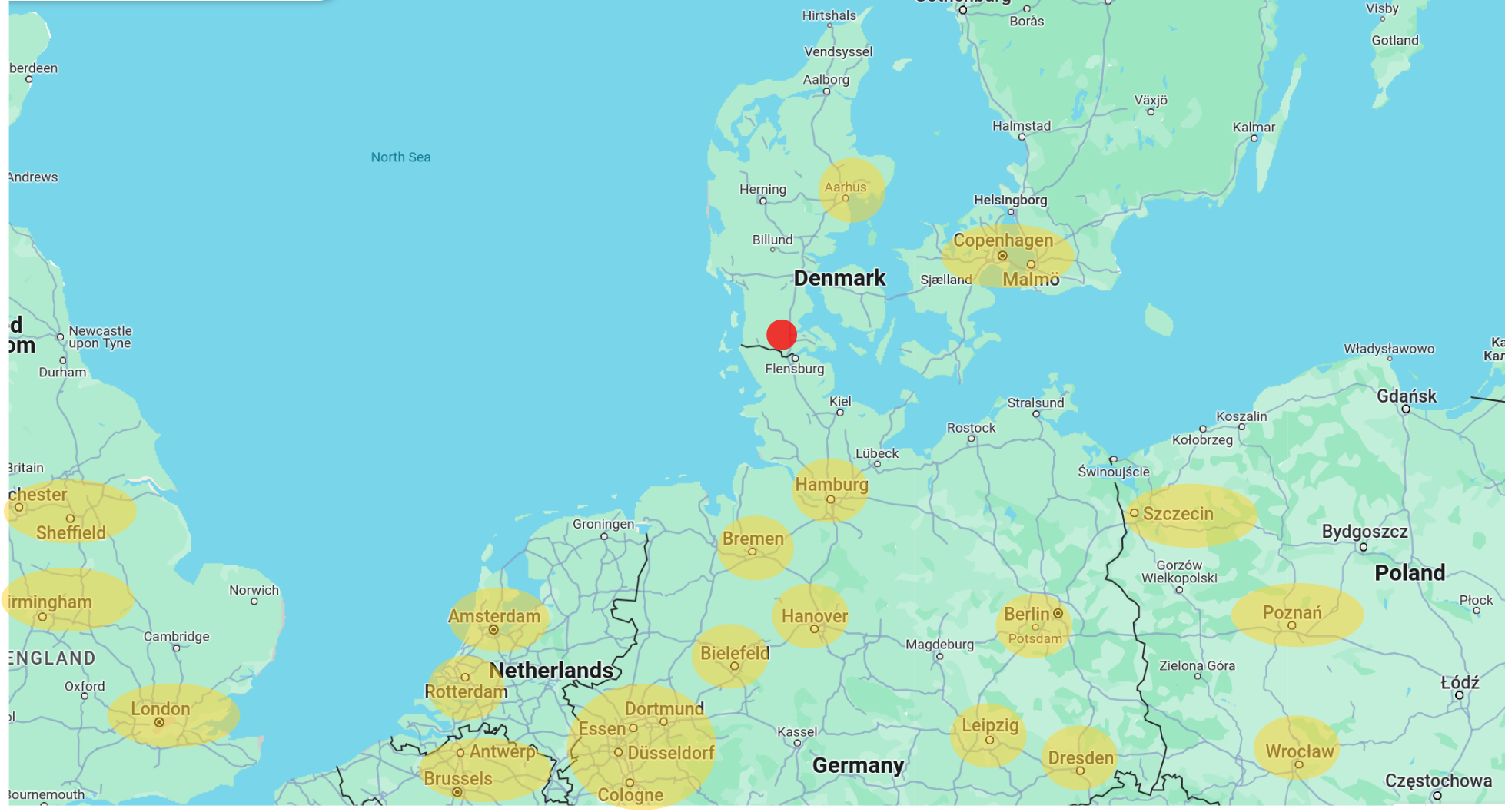
One of Southern Jutland's most significant geographic advantages is its proximity to some of Europe's largest and most economically significant markets. Being centrally located within Scandinavia and just a short distance from major German cities like Hamburg and Berlin, Southern Jutland is strategically placed to serve and access the vast European market efficiently.
Market reach
The region's central position allows businesses to reduce transportation times and costs, enabling quicker market access and better responsiveness to market changes. This proximity is particularly advantageous for industries requiring just-in-time delivery, such as automotive and electronics.
Infrastructure: bridging Denmark and Germany
Extensive road networks
Southern Jutland is crisscrossed by major highways, including the E45, which runs through Denmark into Germany, forming part of the European route network. This highway is crucial for freight movement, providing direct access to both Scandinavian and European destinations. Additionally, the region’s roads connect seamlessly with local and national networks, ensuring efficient distribution of goods and services.
Rail links
The rail infrastructure in Southern Jutland includes significant international railway lines that facilitate the movement of both goods and passengers across Europe. These rail networks are integrated with Europe’s broader rail systems, providing direct links to major ports and cities. This connectivity not only supports the local economy but also enhances the region's logistical capabilities.
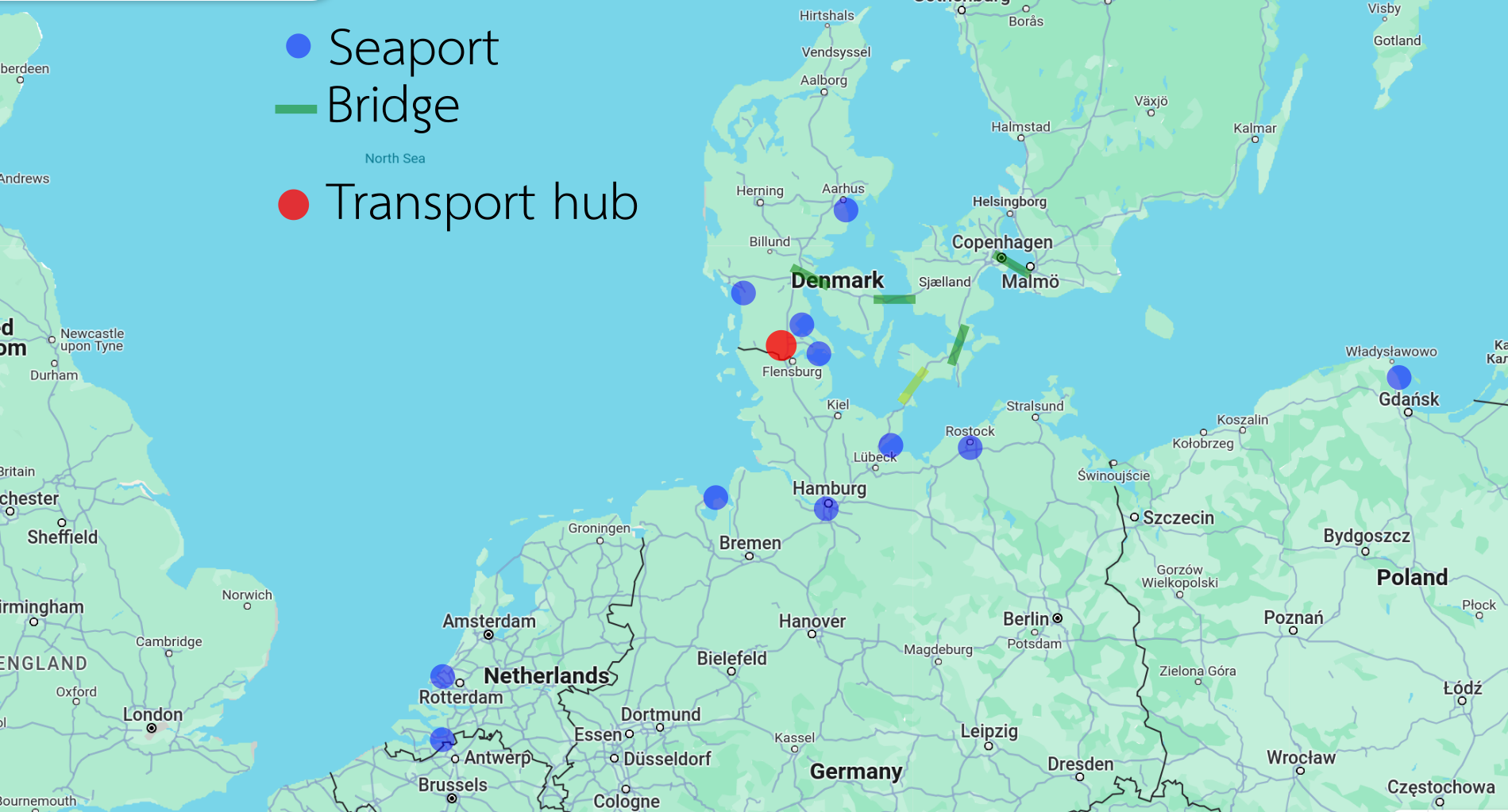
Ports and logistics
The proximity to major Baltic and North Sea ports further enhances Southern Jutland’s logistical advantages. Ports such as Esbjerg on the Danish side and Flensburg on the German side offer critical gateways for maritime trade. These ports are equipped to handle a diverse range of cargo, from bulk commodities to general cargo and container shipping, linking Southern Jutland directly to global trade routes.
Movement of goods: Enhanced by infrastructure
Efficient logistics
The combination of extensive road and rail networks with nearby ports facilitates an efficient logistics framework in Southern Jutland. This infrastructure supports a smooth flow of goods within the region and beyond, boosting its capacity as a logistics and distribution hub.
Cross-border trade
Southern Jutland’s infrastructure also plays a pivotal role in simplifying cross-border trade between Denmark and Germany. Seamless transport links enable businesses to navigate the logistical complexities of international trade with ease, benefiting from reduced barriers and enhanced cooperation between the two countries.
Conclusion
Southern Jutland’s geographic position at the heart of Scandinavia offers unique advantages that are magnified by its exceptional infrastructure. Straddling the dynamic border of Denmark and Germany, the region effectively harnesses its location to provide vital access to major European markets and facilitate the efficient movement of goods across its extensive transport networks. As Europe continues to grow and integrate, Southern Jutland will undoubtedly remain a key player in fostering economic growth and connectivity across the continent.